ASPL Manual v 1.00
© 2024 by SetSphere.COM
7. 2f%U aligns two sequences based on their elements union
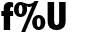
f%U a1 | a1 a2 | a1 a2 a3 where a1 | a1 a2 | a1 a2 a3 are set variables
f%U`mtm~ a1 | a1 a2 | a1 a2 a3
f%U/mtm~ a1 | a1 a2 | a1 a2 a3
f%U
When specified by itself then the operation is performed on the object on top of the stack and the one that is one below it, then the result is pushed on the stack
seqop seqoid 123 notcommu ins:H_H_H text:alignment
Use the operator f%U to align two set variables according to their elements, and display their alignment on the terminal. It is assumed that each set variable has one group label, otherwise the first group (in the set variable) is explicitly implied. If you specify two set variables that have the same named group label, then you need to labinate the operator. If the operator f%U is followed by three set variables then the alignment is performed on the datasets resulted by concatenating the third variable to the first and to the second. Hence this is similar to performing an alignment after joining with an "and" operation the first variable and the third variable, and the second variable and the third variable. You can change the sequence alignment algorithm selectively. The sequence alignment can be selected: the command sequencing lcs selects the algorithm for the longest common sequence, and the command sequencing ssa selects the algorithm for the sequence similarity analysis.
f%U EXAMPLEIn this example we will compare the files in two directories by displaying their sequence alignment. We will start ASPL by loading the WS1 workspace, then we will issue the command f%U to display the alignment of the elements (which are the files) between the two set variables a1 and a2.
f%U OPERATION# aspl WS1
(start ASPL loading the sample workspace WS1 )
① aspl>
sequencing
(show what sequence alignment algorithm is used)
② aspl>
sequencing ssa
(set the sequence alignment algorithm to sequence similarity analysis)
③ aspl>
f%U a1 a2
(show the alignment of the elements between a1 and a2)
④ aspl>
sequencing lcs
(set the sequence alignment algorithm to longest common sequence)
⑤ aspl>
f%U a1 a2
(show the alignment of the elements between a1 and a2)
● Tickable Predicates for f%U
This f%U is tickable with predicates that are shown in the following table:
a yellow note
f%U`_ aligns two sequences based on their elements union f%U`c= aligns two sequences based on their elements union such that they have the same checksum f%U`c~ aligns two sequences based on their elements union such that they have different checksums f%U`c~~ aligns two sequences based on their elements union such that they have all over different checksums f%U`h= aligns two sequences based on their elements union such that they have the same entropy f%U`h~ aligns two sequences based on their elements union such that they have different entropies f%U`h~~ aligns two sequences based on their elements union such that they have all over different entropies f%U`mtm= aligns two sequences based on their elements union such that they have the same make time f%U`mtm~ aligns two sequences based on their elements union such that they have different make times f%U`mtm~~ aligns two sequences based on their elements union such that they have all over different make times f%U`mtm< aligns two sequences based on their elements union such that they have a prior make time f%U`mtm<= aligns two sequences based on their elements union such that they have prior or same make time f%U`mtm> aligns two sequences based on their elements union such that they have more recent make time f%U`mtm>= aligns two sequences based on their elements union such that they have more recent or same make time f%U`ks= aligns two sequences based on their elements union such that they have the same ksum f%U`ks~ aligns two sequences based on their elements union such that they have different ksums f%U`ks~~ aligns two sequences based on their elements union such that they have all over different ksums